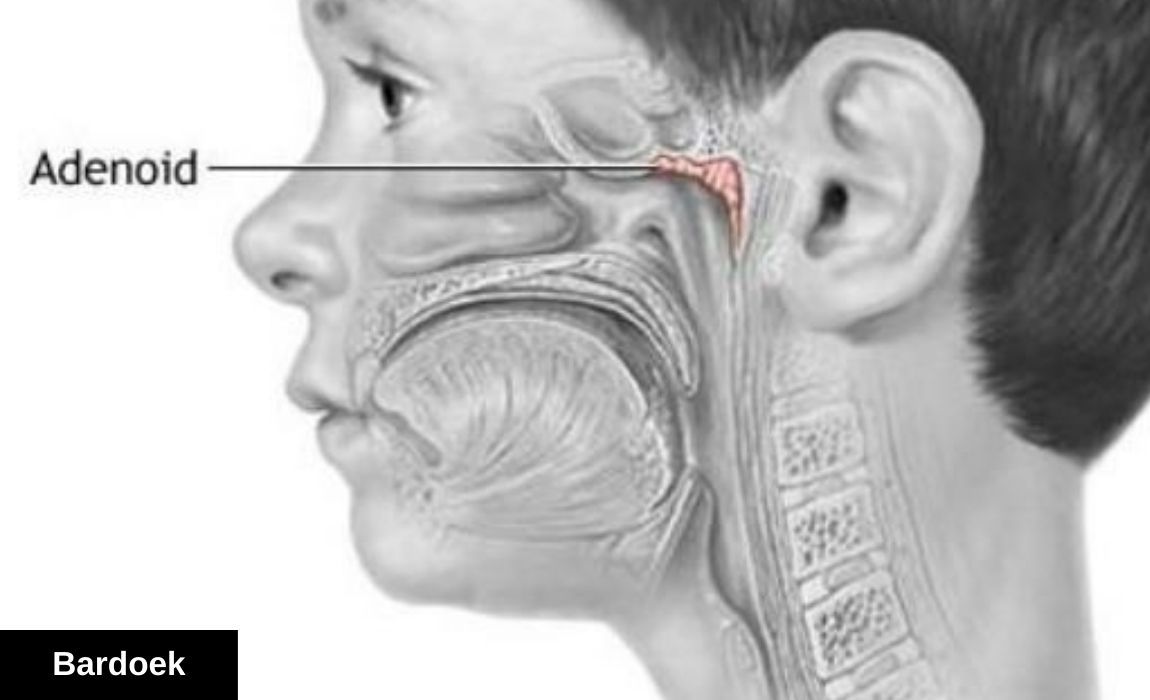
Adenoiditis can feel overwhelming for many parents, especially when symptoms appear suddenly and begin affecting a child’s breathing, sleep, or daily comfort. Although this condition is common, it is often misunderstood or confused with other upper-airway infections. In this powerful and deeply informative guide, we will explore everything you need to know—not only about adenoiditis itself but also how the condition known as Adenoidid relates to inflammation of the adenoids, how it manifests, and how to support your child’s well-being. Parents deserve clarity, and this article aims to provide it in the most accessible and reassuring way possible.
Introduction: Understanding Adenoiditis and the Role of Adenoidid
When parents hear medical terms related to the throat or nasal passages, it is easy to feel uncertain. The word Adenoidid may sound unfamiliar, yet it plays a major role in describing the inflammatory processes that affect the adenoids. These tiny yet powerful immune glands sit behind the nose and help filter harmful particles. When they become swollen or infected, adenoiditis occurs. This condition can disrupt breathing, cause persistent congestion, and lead to nighttime sleep problems. By learning the early signs and knowing how contributes to these symptoms, parents can act quickly and decisively.
What Are the Adenoids and Why Is Adenoidid Significant?
Adenoids are patches of lymphatic tissue located strategically where the nose meets the throat. Because they encounter every breath of air a child takes, they are exposed to viruses, bacteria, and allergens. This makes them active defenders in the immune system. However, their important function also makes them vulnerable to inflammation. The term Adenoidid refers to irritation and swelling that target these glands, particularly in children whose immune systems are still developing. Understanding this structure helps parents grasp why infections escalate quickly and why symptoms can be persistent.
Early Symptoms Parents Should Never Ignore
Symptoms related to Adenoidid and adenoiditis often appear subtly. Children may start breathing through their mouths more frequently—a sign the nasal passages are obstructed. Snoring is another common clue. Because swollen adenoids narrow airflow, nighttime breathing becomes difficult, leading to loud sleep sounds or sudden awakenings. Persistent congestion, bad breath, and a nasal-sounding voice are also hallmark indicators. When progresses, the inflammation can spread toward the ears, causing discomfort or repeated infections. Identifying these early symptoms prevents complications and ensures proper medical care.
How Doctors Diagnose Adenoiditis and Recognize Adenoidid

Diagnosis begins with a careful review of symptoms. Doctors will ask about sleep patterns, breathing difficulties, and the frequency of colds or ear infections. Because the adenoids are not easy to see directly, physicians often rely on imaging tools such as X-rays or flexible nasopharyngoscopy to assess swelling. Testing may also determine whether Adenoidid is caused by bacterial or viral infections. In some cases, allergy evaluation is necessary because inflammation can be triggered by chronic exposure to irritants. Accurate diagnosis leads to targeted treatment that helps children recover faster.
Why Children Are More Prone to Adenoidid
Children experience adenoid problems more often because their adenoids are relatively larger and more active compared to adults. The immune system in childhood depends heavily on lymphatic tissues like the tonsils and adenoids. As a result, exposure to germs at school or daycare increases the likelihood of Adenoidid developing. Frequent upper respiratory infections also contribute to inflammation. Over time, these glands naturally shrink, which is why adenoiditis is far less common in adults. Understanding this developmental process helps parents predict when symptoms are most likely to arise.
Treatment Options: From Home Care to Medical Intervention
Mild cases of adenoiditis can respond well to supportive care. Hydration, rest, and humidifiers can ease discomfort. Saline sprays help clear nasal passages, reducing irritation caused by Adenoidid. When bacterial infection is the culprit, doctors may prescribe antibiotics. Anti-inflammatory medications or nasal corticosteroid sprays can also reduce swelling. For chronic or severe cases—especially when breathing or sleep is affected—surgical removal of the adenoids may be recommended. This procedure, known as adenoidectomy, provides long-term relief and improves airflow dramatically.
How Surgery Helps When Adenoidid Becomes Severe
Adenoidectomy is one of the most common pediatric procedures. Surgeons remove the swollen tissue through the mouth without external incisions. The decision to pursue surgery typically occurs when repeated episodes of interfere with a child’s development, hearing, or quality of sleep. Recovery is generally smooth, with most children returning to normal activities within a week. Parents often report dramatic improvements in breathing, energy levels, and nighttime rest—not only for the child but for the entire household.
Long-Term Effects of Untreated Adenoidid

Left untreated, chronic inflammation can trigger long-lasting issues. Persistent Adenoidid may disrupt sleep cycles, leading to fatigue, irritability, and difficulty focusing at school. Ear infections may become frequent because swollen adenoids block the Eustachian tubes. Speech development can also be affected due to nasal obstruction. Recognizing the potential complications highlights why timely diagnosis is essential. Fortunately, with proper treatment, these long-term effects can be avoided.
The Connection Between Allergies and Adenoidid
Seasonal allergies or environmental triggers often worsen adenoid swelling. Pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or pollution can all inflame the delicate tissues. When allergies and Adenoidid interact, symptoms become more persistent. Managing allergy triggers—through medication, air purifiers, or environmental adjustments—reduces the burden on the immune system. Many children experience dramatic relief when both allergy management and adenoid treatment are combined.
How Adenoidid Affects Breathing and Sleep
Children suffering from Adenoidid often struggle with airflow during sleep. This leads to snoring, restless nights, or episodes resembling sleep apnea. Poor sleep affects behavior, memory, and physical growth. Reduced airflow may also force children to breathe through their mouths, impacting dental development over time. Treating inflammation early restores healthy breathing patterns and improves emotional well-being.
Immune System Impact: Why Adenoidid Weakens Defenses

Although adenoids are designed to strengthen immunity, chronic inflammation has the opposite effect. When Adenoidid persists, the glands struggle to filter out pathogens effectively. This makes children more vulnerable to colds, sinus infections, and ear problems. Supportive care, nutrition, and hydration help the immune system function at its best while recovery occurs.
Prevention Strategies Every Parent Should Know
Simple habits reduce the likelihood of infections. Washing hands regularly, avoiding smoke exposure, and keeping living spaces clean minimize irritation. Nutritious diets rich in vitamins help protect against illnesses that trigger Adenoidid. Encouraging good sleep habits also strengthens immunity. Parents who stay alert to early symptoms can intervene before the condition escalates.
Adenoidid in Adults: Rare but Possible
Although uncommon, adults can experience inflammation of the adenoids. Symptoms are often similar but may present alongside chronic sinus issues or post-nasal drip. Adults exposed to pollutants or suffering from untreated allergies may be more susceptible. Awareness ensures timely medical evaluation.
Supporting a Child Emotionally During Adenoidid
Children may feel anxious when symptoms disrupt their daily routine. Reassuring them, explaining procedures gently, and keeping them involved in care routines helps build confidence. Emotional support speeds recovery just as much as physical treatment when coping with Adenoidid.
Conclusion
Understanding adenoiditis and the broader concept of Adenoidid equips parents to take immediate, effective action. With awareness, prevention, and professional guidance, this condition becomes manageable—often with excellent outcomes. Empowered parents can make informed decisions that safeguard their child’s breathing, sleep, and long-term health.
FAQs About Adenoidid
1. What makes Adenoidid different from adenoiditis?
Adenoiditis refers specifically to infection or inflammation of the adenoids. Adenoidid, while related, is often used to describe the inflammatory processes and symptoms associated with the glands. In practical terms, both involve swelling, difficulty breathing, and immune response issues.
2. How long does Adenoidid typically last in children?
Duration varies. Viral inflammation often resolves within 1–2 weeks, while bacterial causes may persist until treated with antibiotics. Chronic can last months if underlying allergies or repeated infections are not addressed.
3. Can Adenoidid cause hearing problems?
Yes. Swollen adenoids can block the Eustachian tubes, trapping fluid behind the eardrum. Over time, this leads to ear infections or temporary hearing loss. Treating often improves ear function dramatically.
4. Is surgery always needed to treat Adenoidid?
No. Many children recover using medication, hydration, and supportive home care. Surgery becomes necessary only when causes breathing problems, sleep disturbances, or recurring infections.
5. Can adults develop Adenoidid even after childhood?
Although rare, adults can develop inflammation due to allergies, infection, or sinus conditions. Adults experiencing persistent congestion should be evaluated for possible.
6. Is Adenoidid contagious?
The condition itself isn’t contagious, but the viruses or bacteria that cause Adenoidid may be. Practicing good hygiene helps reduce the spread of infectious agents within families.
7. What lifestyle habits help prevent repeated Adenoidid episodes?
Clean air, reduced allergen exposure, good hydration, balanced nutrition, and frequent handwashing all reduce risk. Maintaining a healthy environment helps minimize triggers that lead to chronic Adenoidid.